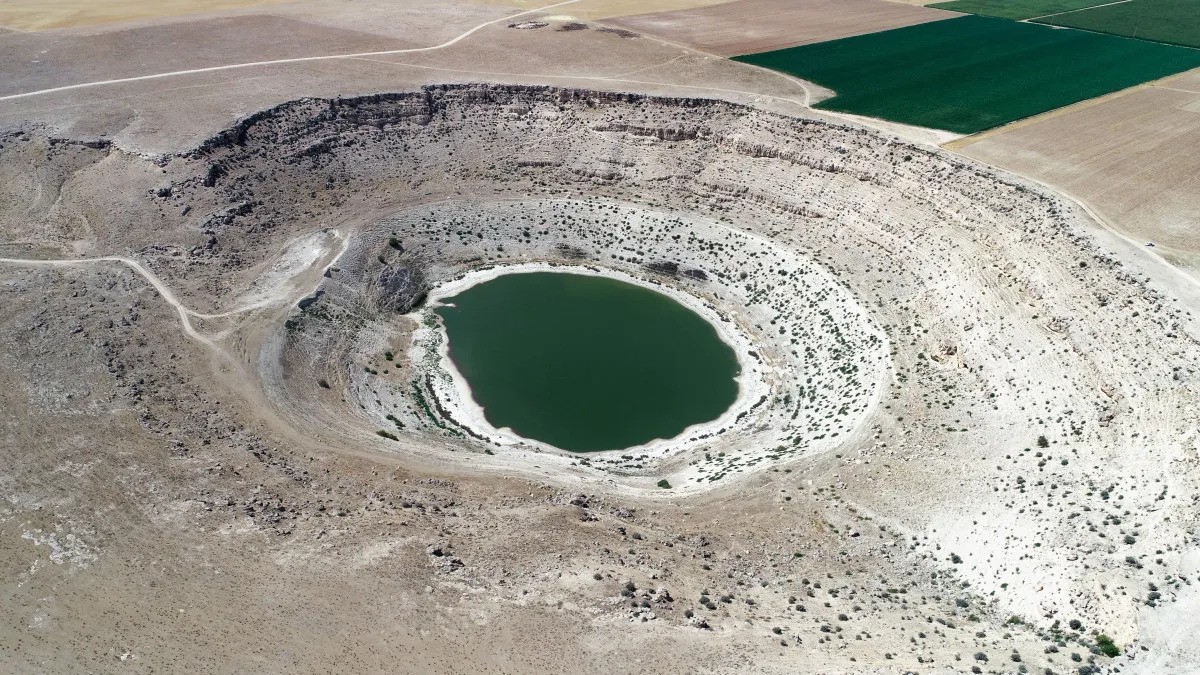
At first glance, Meyil Obruk Lake might look like just another peaceful blue patch nestled in the Konya Plain of Turkey. But here’s what makes it jaw-dropping: this unassuming lake plunges to an astonishing depth of 104 meters. Let that sink in (pun intended) — that’s taller than a 30-story building.
So, what makes Meyil Obruk so unusually deep? Surprisingly, it’s not volcanic activity or a manmade excavation. It’s something more mysterious — and even more powerful — happening silently beneath our feet.
The quiet collapse beneath your feet
Imagine walking across solid ground, only to discover that, below you, water has been secretly gnawing away at the bedrock for centuries. That’s how you get a sinkhole lake like Meyil Obruk.
The region where Meyil Obruk sits is part of a karstic landscape — a geological setting dominated by rocks such as limestone and gypsum, which slowly dissolve in groundwater over time. This process is known as karstification.
Here’s how it works:
- Rainwater absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and soil, forming a weak carbonic acid.
- This slightly acidic water seeps underground and dissolves the soluble rocks below.
- Over time, cavities form and grow in size, eventually creating huge underground voids.
- When the “ceiling” of these voids weakens, it suddenly collapses — forming a sinkhole.
- Then nature steps in: groundwater fills the pit, creating a lake.
This is exactly how Meyil Obruk formed — not from an explosion, but from erosion, pressure, time, and gravity.
How Meyil Obruk is different from other lakes
You’ve probably seen crater lakes and volcanic calderas around the world. But Meyil Obruk tells a different story. Unlike maar lakes formed by volcanic eruptions, this lake has nothing to do with magma. Its depth is a direct result of dissolution and collapse, making it one of the purest examples of a karst sinkhole lake in Turkey.
A quick comparison:
- Meyil Obruk Lake: Formed by karst processes in gypsum and limestone.
- Maar Lakes: Formed by explosive volcanic interactions between magma and groundwater.
This makes Meyil Obruk not just a geological wonder — but a living laboratory for earth scientists.
Experiments and findings from past studies
Over the years, geologists and researchers have studied Meyil Obruk to gain a deeper understanding of its features, not just its depth. Notable experiments include:
- Hydrogeological sampling (2012): Scientists tested the water to understand its mineral content and how groundwater levels fluctuate seasonally. Results showed that water levels were linked to nearby agricultural pumping and rainfall patterns.
- Geophysical surveys (2016): Subsurface scans confirmed that large voids still exist around the lake, raising concerns that more sinkholes could form in the future.
- Speleological studies (2019): Cave divers explored parts of the lakebed, discovering multiple submerged caverns — a clear indicator of ongoing karstification underneath.
These studies not only highlight the lake’s unpredictable nature but also its vulnerability in the face of climate change and human-triggered groundwater depletion.
The deeper truth
Meyil Obruk may look calm on the surface, but it stands as a dramatic reminder of the forces working quietly beneath us. Karst landscapes don’t just shape geography — they reshape how we understand the Earth’s surface and its hidden vulnerabilities.
So next time you’re standing near what seems like flat, solid ground, you might want to ask yourself: what’s happening below?
Because, as Meyil Obruk shows us, sometimes, the deepest scars in nature lie beneath the stillest waters.



Leave a Comment